DIGEST focuses on the integration of grid energy storage into the grid. Specifically, the project aims to demonstrate the carbon emissions savings possible by optimally locating and operating storage to avoid curtailment of renewables and additional fossil fuel generation. Energy storage can provide many benefits to the power grid, and it is projected that substantial storage will be required to meet UK net-zero targets (Aunedi 2021). However, it is not clear whether the financial and environmental advantages of storage currently align (e.g., if storage is placed far from excess renewable generation, on the other side of a congested network).
The DIGEST project aims to test two hypotheses:
DIGEST has five key objectives, structured into four work packages:

Figure 1. Work packages
DIGEST advances and links leading GB national network models:
Thomas Morstyn and team have developed a high-fidelity 2000 node GB transmission network model integrated with a Balancing Mechanism market model and Elexon unit-level data.
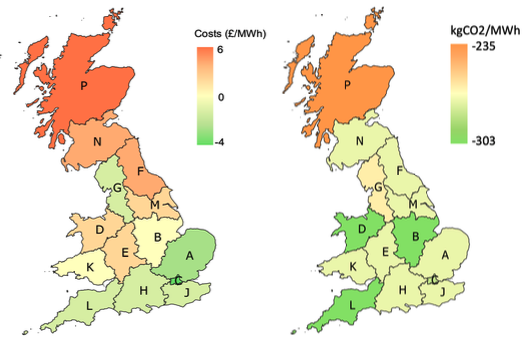
Figure 2. Cost and carbon implications of deploying additional wind capacity in different locations on the GB grid
Marko Aunedi and team are using an established whole-electricity system model to quantify cost implications across different segments of electricity system using mixed integer linear programming. As part of this project this will be extended to represent the GB transmission network with a higher granularity.
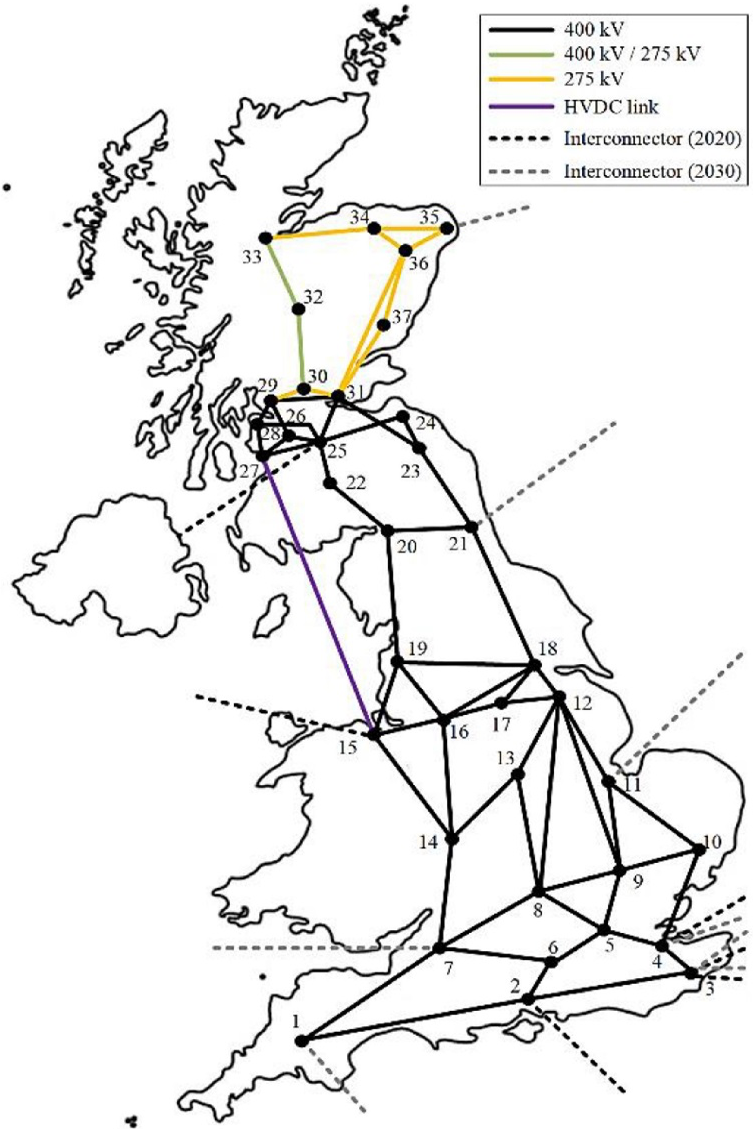
Figure 3. 37 nodes for location specific assessment of storage on the GB grid
Aunedi, Wills, Strbac, Green, “Net-zero GB electricity: cost-optimal generation and storage mix”, Energy Futures Lab White Paper, June 2021.